Share on:
What is boiling?
Vaporization is the conversion of a substance from the liquid or solid phase into the gaseous (vapour) phase. Heat must be supplied to a solid or liquid to effect vaporization.
There are three different states of matter: solid, liquid and gas. They differ in their molecules bounding forces. A molecule consists of a collection of two or more atoms. For example, a water molecule is H2O (two hydrogen atoms attached to a single oxygen atom). The driving force that encourages atoms and molecules to combine in certain way is energy.
In a solid, the particles are closely packed together. The forces between particles are strong so that the particles cannot move freely. As a result, a solid has a stable, definite shape, and a definite volume. Gas molecules have very weak or no bonds at all, they can move freely and fast.
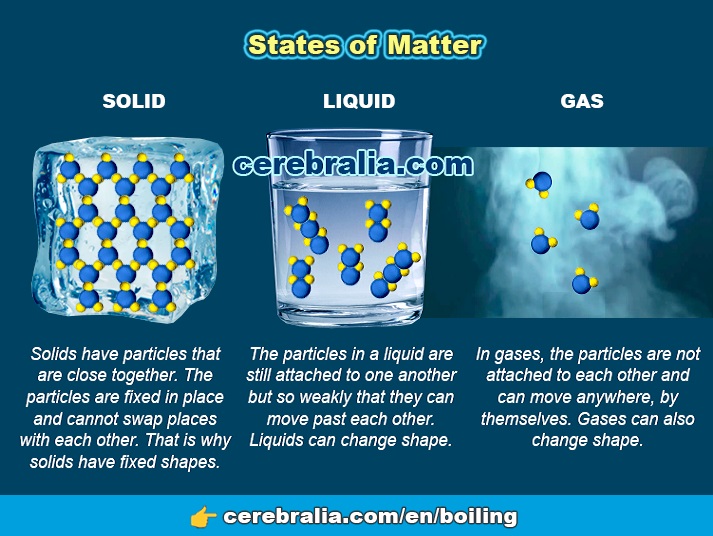
A gas has no definite shape or volume, but occupies the entire container in which it is confined. A liquid may be converted to a gas by heating at constant pressure to the boiling point, or else by reducing the pressure at constant temperature.
Boiling is the rapid vaporization of a liquid, which occurs when a liquid is heated to its boiling point. The boiling point of a liquid depends on temperature, atmospheric pressure, and the vapor pressure of the liquid.
Difference between boiling and evaporation
When we spread wet clothes on a rope or wire, they dry up after some time, this is because water present in wet clothes evaporates by receiving heat from the sun. Water from wet roads and puddles also dries up and disappears by forming water vapour by the process of evaporation.
By heating the water over the fire, we increase its temperature making the molecules move faster. When the liquid starts to boil (212 °F), the more energetic molecules change to a gas, spread out, and form bubbles. These rise to the surface and is released into the atmosphere as water vapor.

The main differences between evaporation and boiling are:
- Evaporation occurs slowly and gradually. Boiling occurs more quickly.
- Evaporation takes place at any given temperature. Boiling always occurs at the boiling point of a liquid.
- Evaporation only takes place on the surface of the liquid. Boiling occurs throughout the liquid.
- The main sign of boiling is the formation of bubbles. They do not appear in evaporation.
- When evaporation takes place, the temperature of the liquid body decreases. The temperature remains constant throughout the boiling process.
- Evaporation takes place as long as the air above the liquid remains unsaturated. Boiling takes place when the internal liquid pressure is equal to the external pressure.
Temperature and boiling
Boiling requires energy to change from a liquid to a gas. In addition, gas molecules leaving the liquid remove thermal energy from the liquid. Therefore the temperature of the liquid remains constant during boiling. For example, water will remain at 212 ºF (at a pressure of 1 atm or 101.3 kPa) while boiling.
Atmospheric pressure and boiling
The pressure of gas above a liquid affects the boiling point. In an open system this is called atmospheric pressure. The greater the pressure, the more energy required for liquids to boil, and the higher the boiling point.
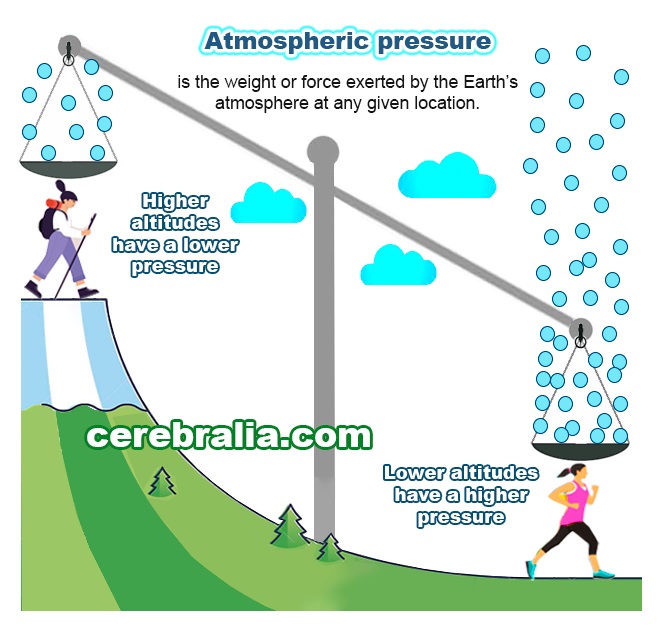
This can be visualized as air molecules colliding with the surface of the liquid and creating pressure. This pressure is transmitted throughout the liquid and makes it more difficult for bubbles to form and for boiling to take place. If the pressure is reduced, the liquid requires less energy to change to a gaseous phase, and boiling occurs at a lower temperature.
| Location | Atmospheric pressure | boiling point for water | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Earth at Sea Level | 101.3 kPa | 100 °C | 212 °F |
| Mount Everest Summit | 33.7 kPa | 70 °C | 158 °F |
| Mars (average) | 0.6 kPa | 10 °C | 50 °F |
| Venus (average) | 9200 kPa | 300 °C | 572 °F |
The opposite happens in a pressure cooker. The atmospheric pressure inside the pot is boosted by the trapped steam. This causes the boiling point of the water to increase from the regular 212 degrees Fahrenheit to 250 degrees Fahrenheit. This elevated temperature is the reason foods cook faster in a pressure cooker.
Vapor pressure and boiling
The molecules leaving a liquid through evaporation create an upward pressure as they collide with air molecules. This upward push is called the vapor pressure. Different substances have different vapor pressures and therefore different boiling points.
The vapor pressure of a liquid lowers the amount of pressure exerted on the liquid by the atmosphere. As a result, liquids with high vapor pressures have lower boiling points. Vapor pressure can be increased by heating a liquid and causing more molecules to enter the atmosphere. At the point where the vapor pressure is equal to the atmospheric pressure boiling will begin.
